Working Principle of Four Stroke (Diesel/Petrol) Engine
Working Principle of Four Stroke Engine
The various strokes
in four stroke engine are
- Suction stroke
- Compression stroke
- Power stroke
- Exhaust stroke
 |
| © Mechanical Booster |
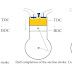
01. Suction Stroke:
- Piston moves from TDC to BDC
- Opening of intake valve
- Suction of the air or air fuel-mixture ( air in diesel engine and air-fuel mixture in petrol engine)
In
suction stroke what happens, first the piston moves from TDC to BDC. As the
piston moves the inlet valve opens and the air fuel mixture in case of petrol
engine and only air in diesel engine enters into the cylinder. The exhaust
valve remains closed during this stroke.
02. Compression Stroke:
 |
| © Mechanical Booster |
- Piston moves from BDC to TDC
- Compression of air or air-fuel mixture (air in diesel engine and air-fuel mixture in petrol engine)
- Intake and Exhaust valve remains closed
In
compression stroke, the piston moves from BDC to TDC. The inlet and exhaust
valve remains closed during this stroke. As the piston moves upward (from BDC
to TDC) the compression of air- fuel mixture in case of petrol engine and only
air in case of diesel engine takes place. The compression processes completes
when piston reaches to the TDC. The compression is done to increase the temperature
of the air or air-fuel mixture. The temperature is increased so that it can
easily catch fire during sparking in case of petrol engine and spraying of
diesel in case of diesel engine.
03. Expansion/Power Stroke:
 |
| © Mechanical Booster |
- Sparking and burning of the air-fuel mixture in Petrol engine.
- Burning of diesel by the hot gases.
- Piston moves from TDC to BDC.
- Intake and Exhaust valve remains closed.
More read:
Petrol engine: The air-fuel mixture is ignited by the spark plug. Due to
the ignition the burning process starts. The burning of the air-fuel mixture
creates a very high pressure burnt gases. This high pressure burnt gases exerts
a thrust on the top face of the piston and it starts to move downward from TDC
to BDC. This is the power stroke of the engine. In this stroke we get power
which is utilized to run the vehicle. The intake and exhaust valve remains
closed during this stroke.
Diesel engine: As the Piston approaches TDC the injection of the diesel in
the form of spray by fuel injector takes place. As the diesel sprayed by the
fuel injector come in contact with the hot compressed gases it catches fire and
burning processes starts. Due to burning high pressure hot burnt gases
originates and it puts a very high thrust on the top face of the piston. Due
the thrust impact on the piston it starts to move in downward direction i.e.
form TDC to BDC.
04. Exhaust Stroke:
 |
| © Mechanical Booster |
- Piston moves from DBC to TDC.
- Opening of the Exhaust Valve.
- Escaping of the hot burnt gases through exhaust valve.
In this stroke the piston moves
upward i.e. from TDC to BDC. As the piston moves upward the exhaust valve opens
and all the burnt gases left after power stroke starts escaping out of the
cylinder. The burnt gases escape out in the environment through exhaust Valve.
When the piston reaches at TDC the exhaust process completes. And after this
again all the four stroke repeat themselves. ©
www.mechanicalbooster.com








No comments